Alternatives for Mobile App Development: Streamlining Testing with Tunneling Services
Beyond Native: Smart Alternatives for Mobile App Development & How Tunneling Streamlines Testing
The global demand for mobile applications is insatiable. From e-commerce and finance to entertainment and productivity, apps have become the primary digital touchpoint for businesses and consumers alike. However, the traditional path of mobile app development—building separate, native applications for iOS and Android—is a resource-intensive endeavor. It demands significant time, a large budget, and specialized development teams for each platform. For many startups and even established enterprises, this barrier to entry is simply too high.
Fortunately, the development landscape has evolved. A new generation of powerful alternatives has emerged, offering more efficient, cost-effective, and faster ways to bring an app to market. These approaches, including cross-platform, hybrid, and Progressive Web Apps (PWAs), are changing the game.
But building the app is only one part of the equation. Effective and efficient testing is the bedrock of a successful application, ensuring a bug-free, high-performance user experience. This is where another crucial innovation comes into play: tunneling services. These tools act as a secure bridge between your local development environment and the public internet, revolutionizing how developers test, share, and collaborate. This article explores the leading alternatives to native app development and dives deep into how tunneling services can dramatically streamline your testing workflow, saving you time, money, and headaches.
The Native App Conundrum: Why Seek Alternatives?
Before we explore the alternatives, it’s essential to understand the traditional approach. Native app development involves writing code specifically for a single platform’s operating system. For iOS, this means using languages like Swift or Objective-C with Apple’s Xcode IDE. For Android, it’s Kotlin or Java using Android Studio.
The Allure of Native Development
There’s a reason native development has long been considered the gold standard. The benefits are significant:
- Peak Performance: Native apps are compiled into the device’s native machine code, allowing them to run incredibly fast and smoothly. They can fully leverage the device’s processing power, making them ideal for graphically intensive applications like games or complex animations.
- Optimal User Experience (UX): Because native apps are built using the platform’s standard UI/UX components, they look and feel exactly as users expect. They adhere to the design guidelines of iOS and Android, providing a familiar and intuitive experience.
- Full API and Hardware Access: Native development provides unrestricted access to all of the device’s hardware and software features, including the camera, GPS, accelerometer, contacts, and push notifications. This allows for deeply integrated and feature-rich applications.
The High Cost of Going Native
Despite these advantages, the drawbacks of native development are often prohibitive:
- Exorbitant Costs: The most significant hurdle is the cost. You are essentially building two separate applications from scratch. This requires two distinct development teams with specialized skills (iOS and Android), doubling your payroll and operational overhead.
- Extended Time-to-Market: Managing two codebases means longer development cycles. Feature implementation, bug fixing, and updates must be done twice. Coordinating simultaneous feature releases across both platforms can become a logistical nightmare.
- Maintenance Headaches: The work doesn’t stop at launch. Ongoing maintenance, updates for new OS versions, and bug fixes must be consistently managed for both the iOS and Android versions, further inflating long-term costs.
For many businesses, these challenges make a pure native approach impractical. The need for a more unified, efficient, and cost-effective solution has paved the way for a host of powerful alternatives.
A Deep Dive into Mobile App Development Alternatives
Modern development frameworks allow you to build high-quality applications without the burden of managing two separate codebases. Let’s explore the most popular options.
1. Cross-Platform Development
The philosophy of cross-platform development is simple yet powerful: “write once, run anywhere.” Developers write a single codebase using a specific framework, which is then compiled into native code for both iOS and Android. This approach retains much of the performance and feel of a native app while drastically reducing development time and cost.
- React Native: Created by Facebook, React Native is one of the most popular cross-platform frameworks. It allows web developers to leverage their existing JavaScript and React skills to build mobile apps. Its component-based architecture and features like “Hot Reloading” (which allows you to see code changes instantly without recompiling the entire app) make for a highly efficient development experience. Apps like Instagram, Shopify, and Tesla are built with React Native.
- Flutter: Developed by Google, Flutter has rapidly gained traction for its stunning UIs and exceptional performance. It uses the Dart programming language and a unique widget-based system that gives developers granular control over every pixel on the screen. Flutter compiles directly to ARM machine code, resulting in performance that is often indistinguishable from native apps. Google Pay, BMW, and Alibaba have used Flutter to power their applications.
- Xamarin: Owned by Microsoft, Xamarin is a strong contender, particularly for enterprises already invested in the .NET ecosystem. It allows developers to use C# to build apps for iOS, Android, and Windows. Xamarin enables the sharing of logic across platforms while still allowing for the creation of platform-specific UIs.
2. Hybrid App Development
Hybrid app development takes a different approach. It involves building an application using standard web technologies—HTML, CSS, and JavaScript—and then wrapping it in a native container known as a WebView. This container allows the web app to be installed on a device and submitted to app stores just like a native app.
- Ionic: The leading hybrid app framework, Ionic provides a library of UI components that are styled to mimic native iOS and Android design patterns. It integrates seamlessly with popular web frameworks like Angular, React, and Vue, allowing teams to leverage their existing web development expertise.
- Apache Cordova (formerly PhoneGap): Cordova is the open-source engine that powers many hybrid apps. It provides a set of JavaScript APIs that act as a bridge, allowing the web code to access native device features like the camera and accelerometer.
The primary advantage of hybrid apps is speed and simplicity. A single web developer can produce a functional app for both platforms in a fraction of the time it would take to go native. However, this often comes at the cost of performance, as WebViews can be less responsive than native components.
3. Progressive Web Apps (PWAs)
PWAs blur the lines between a website and a mobile app. A PWA is essentially a web application that uses modern browser APIs and features to deliver an app-like experience directly in the browser. They don’t require an app store for distribution.
Key features of PWAs include:
- Installable: Users can add the PWA to their home screen with a single tap, creating an icon just like a native app.
- Offline Capability: Through a technology called “service workers,” PWAs can cache content and function even without an internet connection.
- Push Notifications: PWAs can send push notifications to re-engage users.
- Discoverable: Since they are websites, PWAs are indexable by search engines, making them easy to find.
PWAs are an excellent choice for content-driven applications, e-commerce stores, and informational services. While their access to device hardware is more limited than native or cross-platform apps, they offer unparalleled reach and eliminate the friction of app store downloads.
The Unsung Hero: Streamlining Testing with Tunneling Services
Choosing the right development framework is a critical first step. But no matter which path you take, your app’s success hinges on rigorous testing. This is where the development process often hits a major bottleneck.
The Localhost Challenge
Developers typically write and run code on their local machines in an environment known as localhost. This local server is perfect for initial development, but it’s isolated. It’s not accessible from the outside world, which creates a significant problem: How do you test your work-in-progress on a real mobile device?
A physical smartphone is not on the same network as your localhost. This means you can’t simply point the app on your phone to your development server. The traditional workarounds are clunky and inefficient:
- Complex Network Configuration: Fiddling with router settings, firewalls, and IP addresses to try and expose your machine to the local network. This is often unreliable and insecure.
- Deploying to a Staging Server: For every minor code change, you have to push your code, wait for it to build and deploy to a remote server, and only then can you test it. This “code -> commit -> build -> deploy -> test” cycle is painfully slow and stifles rapid iteration.
Enter Tunneling Services: Your Localhost on the World Wide Web
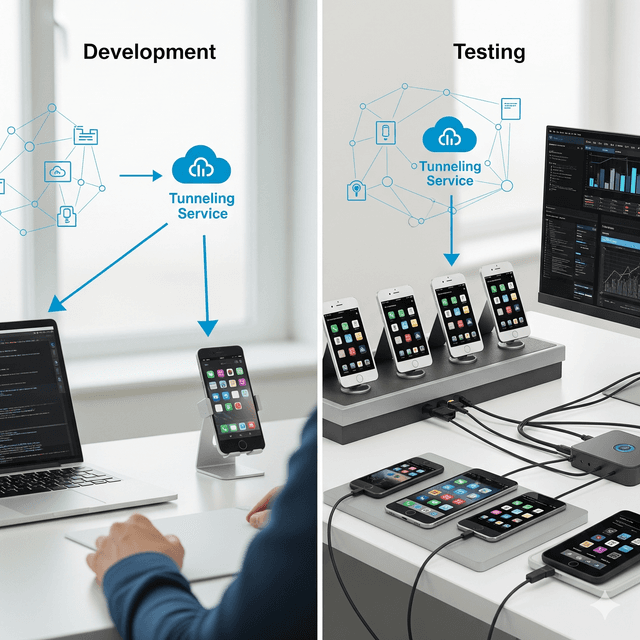
This is precisely the problem that tunneling services solve. A tunneling service creates a secure, encrypted tunnel from a public URL on the internet directly to the localhost server running on your development machine.
Imagine it like this: The tunneling service gives your private localhost a temporary public address. When you run the service’s command-line tool, it connects to its cloud and generates a unique, shareable URL (e.g., https://random-subdomain.ngrok.io). Any request sent to this public URL is instantly and securely forwarded through the tunnel to your application running locally.
The Transformative Benefits of Tunneling for Mobile App Testing
Integrating a tunneling service into your workflow is a game-changer. Here’s why:
1. Seamless Real-Device Testing
Emulators and simulators are useful, but they can’t replicate the nuances of a real device. Performance, touch gestures, network interruptions, and interactions with hardware like the camera or GPS can only be accurately tested on a physical phone. With a tunneling service, you simply configure your mobile app build to point its API requests to the public tunnel URL. Now, you can test your local code on your iPhone or Android device in real-time.
2. Accelerated Iteration and Debugging
The slow deployment cycle is eliminated. You can now follow a much faster workflow: code -> save -> test instantly on a device. Make a change to your backend code, save the file, and the updated behavior is immediately available on the physical device you’re testing with. This dramatically speeds up the process of finding and fixing bugs.
3. Effortless Collaboration and Feedback
Tunneling makes sharing your work-in-progress incredibly simple. Instead of trying to describe a new feature or bug, you can send the secure tunnel URL to anyone, anywhere in the world.
- Client Demos: Show your clients a live, working version of their app without having to deploy anything. Get instant feedback and make changes on the fly.
- QA Teams: Your Quality Assurance team can start testing new features the moment they are developed, using real devices, without any complex setup on their end.
- Design Reviews: Allow UI/UX designers to see their creations implemented on an actual device, ensuring that animations, layouts, and interactions look and feel right.
4. Simplified Webhook Integration
Modern applications frequently integrate with third-party services for payments (Stripe), communications (Twilio), or source control (GitHub). These services often use webhooks to send notifications back to your application when an event occurs (e.g., a payment is processed). For a webhook to work, the third-party service needs a public URL to send the notification to. Tunneling services provide this public URL instantly, allowing you to develop and test webhook integrations entirely on your local machine.
Popular Tunneling Services
- ngrok: The most popular and well-known tunneling service. It’s incredibly easy to set up and offers a powerful free tier, along with paid plans that include features like custom domains and a web interface for inspecting all traffic passing through the tunnel.
- localtunnel: A fantastic open-source alternative that is free and simple to use.
- Cloudflare Tunnel: A highly secure and robust option from the web infrastructure giant Cloudflare. It’s part of a broader suite of developer tools and is an excellent choice for teams that need enterprise-grade security.
Putting It All Together: A Modern Development Workflow
By combining an alternative development approach with a streamlined testing process, you can build better apps faster. Here’s what a modern workflow looks like:
- Choose Your Framework: Select the best alternative for your project (e.g., Flutter for a highly performant, custom UI).
- Develop Locally: Build a new feature or fix a bug on your
localhostenvironment. - Start Your Tunnel: Run a single command in your terminal (e.g.,
ngrok http 3000) to expose your local server to the internet. - Test on a Real Device: Open your mobile app, configured to use the public ngrok URL, and test the new feature on your phone.
- Share and Collaborate: Instantly share the URL with a colleague or client for a live review.
- Iterate Rapidly: Receive feedback, make code changes locally, and see the results update on the device in real-time.
- Deploy with Confidence: Once the feature is fully tested and approved, merge the code and deploy it to your production environment.
Conclusion
The mobile app development landscape is no longer a one-size-fits-all world dominated by native development. Powerful alternatives like React Native, Flutter, Ionic, and PWAs provide flexible, cost-effective, and efficient pathways to building exceptional applications. They empower businesses to reach a wider audience faster and with a leaner budget.
However, building the app is just the beginning. Adopting a modern, agile testing workflow is paramount to success. Tunneling services are a transformative tool in this process, bridging the critical gap between local development and real-world testing. By eliminating slow deployment cycles and enabling seamless real-device testing and collaboration, they empower teams to iterate faster, catch bugs earlier, and ultimately ship higher-quality products. By combining a smart development strategy with a streamlined testing process, you can gain a crucial competitive edge in the bustling world of mobile apps.
Related Topics
Keep building with InstaTunnel
Read the docs for implementation details or compare plans before you ship.